Introduction: why 6G is already on the horizon
It feels like we’ve only just started enjoying the perks of 5G — smoother video calls, faster streaming, and the promise of smart cities. Yet, in the world of technology, there’s never a pause button. Even while 5G is still expanding globally, researchers and telecom giants are already laying the groundwork for its successor: 6G technology.
If 5G was the leap that gave us self-driving cars, industrial automation, and real-time cloud gaming, then 6G is the giant leap that could redefine what it means to be connected. We’re not just talking about speed; we’re talking about a living, breathing network powered by AI, capable of learning and adapting in real time.
Imagine walking into a meeting where your colleague isn’t on a screen but standing next to you as a lifelike hologram. Picture hospitals where surgeons in different countries can operate on the same patient simultaneously through robotic tools. Visualize a world where devices anticipate your needs before you even think about them. That’s the promise of 6G — the backbone of a hyper-connected, immersive, and intelligent future.
6G technology explained: the foundation of next generation wireless connectivity
When we say 6G technology, it’s easy to assume it’s just “faster internet.” But in reality, it’s shaping up to be a fundamental rethinking of how networks are built and used.
Unlike previous generations that focused mainly on boosting speed, 6G aims to create a fully intelligent, self-optimizing network. Let’s break down the core elements that define it:
1. Terahertz spectrum
5G operates mostly in sub-6 GHz and millimeter-wave bands, but 6G will climb even higher — into the terahertz (THz) spectrum, between 100 GHz and 10 THz. Why does this matter? Because higher frequencies mean massive bandwidth, enabling data transfer at up to 1 terabit per second.
Of course, there’s a trade-off: terahertz waves don’t travel far and are easily blocked by walls, meaning we’ll need denser infrastructure like small cells, repeaters, and even satellite support.
2. AI-native networks
While 5G integrates AI for optimization, 6G is being designed as an AI-native system. That means the network itself will “think” — predicting traffic patterns, self-healing outages, and dynamically adjusting resources without human intervention.
This doesn’t just make it faster; it makes it smarter and more energy efficient, which is crucial given the growing demand for sustainability.
3. Integrated land–air–space coverage
5G is mainly ground-based, with some satellite overlap. 6G, on the other hand, is expected to combine satellites, drones, and ground towers into one seamless network. This could provide true global coverage, connecting remote regions that current infrastructure struggles to reach.
4. Extreme connectivity
6G will support billions of devices per square kilometer without network congestion. This is critical for the Internet of Everything — from self-driving cars and delivery drones to smart wearables and holographic entertainment.
5. Sensory internet
One of the most fascinating aspects of 6G is its potential to transmit not just sound and visuals, but touch and even smell data. Imagine playing a game where you feel the textures of objects or shopping online where you can “touch” the fabric virtually.
Why it matters:
6G won’t just be an upgrade — it will serve as the backbone of a fully digital society, where physical and virtual worlds merge seamlessly. If 5G made smartphones powerful, 6G could make entire environments intelligent.
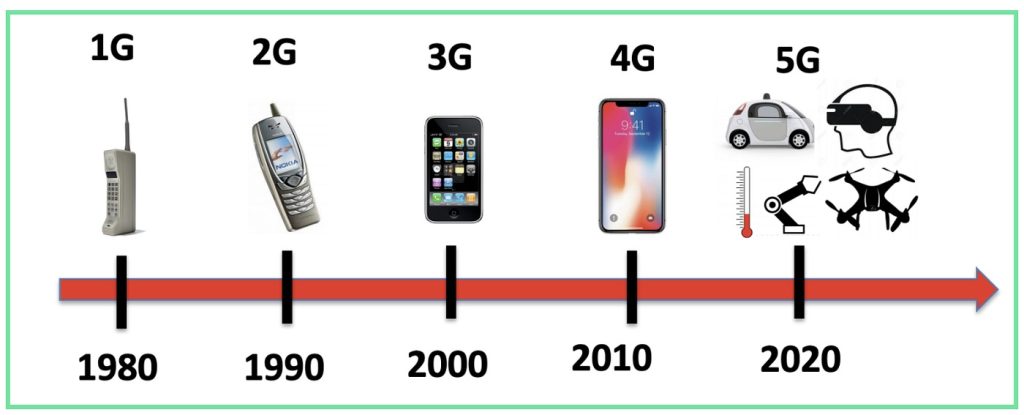
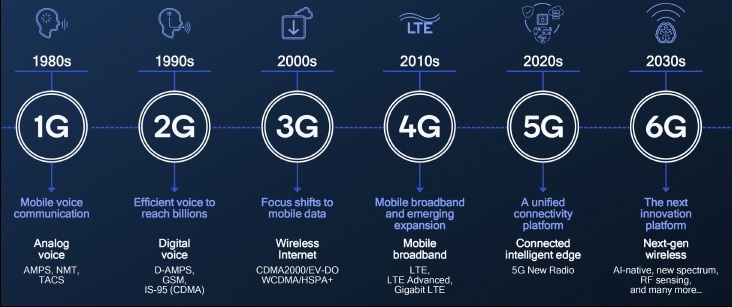
Looking back: how we got from 1G to 5G
To understand why 6G technology is such a big deal, it helps to take a quick trip down memory lane. Each mobile generation wasn’t just about faster connections — it fundamentally changed how we live, work, and communicate.
1G: the analog beginning (1980s)
This was the era of the “brick phone.” 1G gave us basic analog voice calls, but the quality was poor, security was nearly nonexistent, and coverage was spotty. Still, it was revolutionary — people could finally talk on the go.
2G: the rise of digital and texting (1990s)
Enter digital voice and SMS messaging. Suddenly, “texting” became the cool new way to communicate. 2G networks also introduced basic mobile data services like picture messages.
3G: the internet goes mobile (2000s)
This is when the mobile world truly exploded. 3G brought mobile internet, video calling, and faster data speeds, paving the way for smartphones, social media, and mobile email. You could browse the web on the move (slowly, but still!).
4G: the app and streaming revolution (2010s)
If you’ve ever streamed Netflix on the bus or ordered UberEats, thank 4G. With speeds up to 100 Mbps, it fueled app ecosystems, HD video, and cloud services. 4G turned smartphones into pocket-sized computers.
5G: ultra-fast, ultra-connected (2020s)
With gigabit speeds and ultra-low latency, 5G enabled real-time cloud gaming, AR/VR experiences, and IoT growth. Beyond phones, it started powering smart factories, connected cars, and smart cities.
Why this matters for 6G:
Each “G” unlocked entirely new possibilities. 1G let us talk anywhere. 2G made texting a cultural phenomenon. 3G gave us the mobile internet. 4G built the app-driven lifestyle we rely on today. 5G is fueling smart cities and automation.
Now, 6G isn’t just the next step — it’s the leap into a hyper-immersive, AI-driven world, where networks go from being tools we use to an environment we live in.
6G vs 5G speed and performance
The first question people ask about 6G is simple: “How fast is 6G?” The answer: mind-blowingly fast. But speed is just one part of the story — performance also includes latency, reliability, and capacity. Let’s break it down.
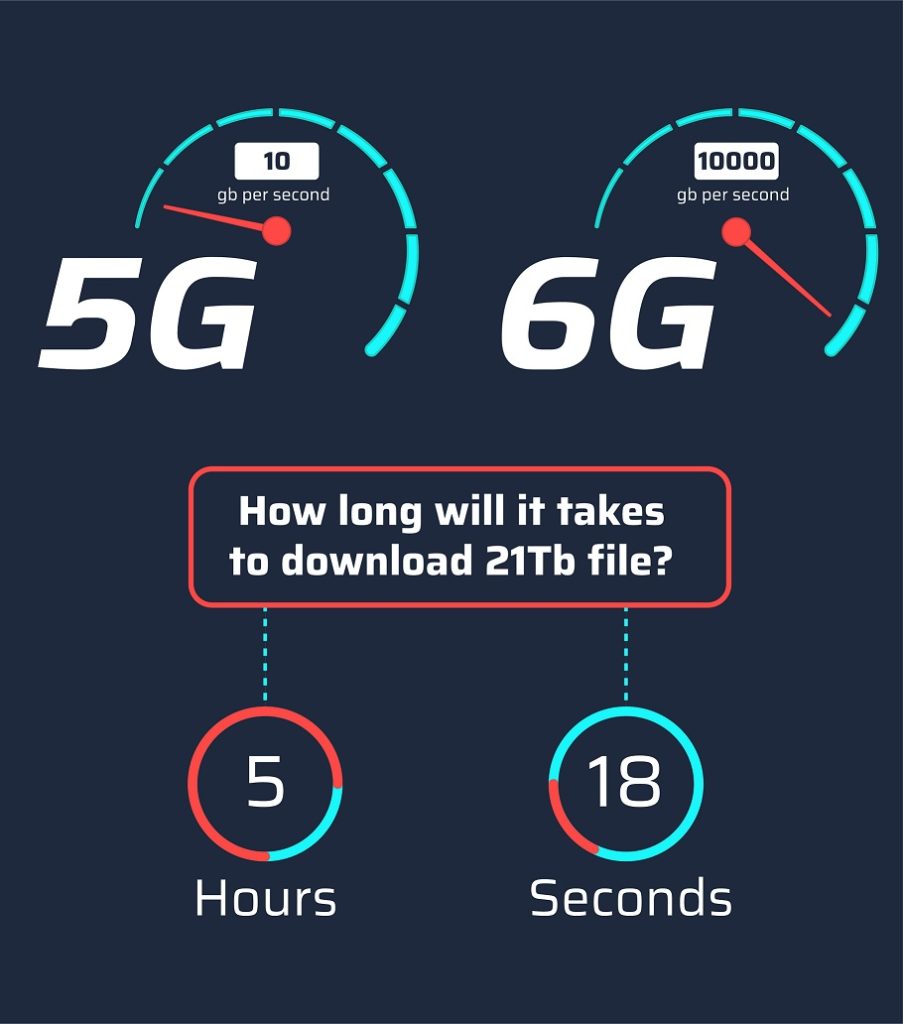
Speed: the headline feature
- 5G peak speeds: Around 10 Gbps under ideal conditions.
- 6G projected speeds: Up to 1 Tbps (1,000 Gbps).
That’s almost 100 times faster. To put that into perspective:
- Downloading a two-hour 8K movie: A few minutes on 5G. Under a second on 6G.
- Uploading a 1TB backup to the cloud: Hours on 5G. Just seconds on 6G.
- Streaming VR/AR games: Smooth, lag-free, and indistinguishable from reality.
Latency: goodbye, lag
Latency is the delay between sending and receiving data.
- 5G latency: 1–10 milliseconds.
- 6G latency: About 1 microsecond — a thousand times faster than the blink of an eye.
This makes communication practically instantaneous. For everyday users, it means lag-free gaming and video calls. For industries, it enables remote surgery, autonomous cars, and real-time industrial automation.
Reliability and capacity
6G will be designed to connect billions of devices per square kilometer without congestion. That means smart cities where sensors, vehicles, drones, and wearables all run simultaneously with zero downtime.
Beyond speed: the sensory internet
Another difference? 5G gives us faster internet. 6G could give us a sensory internet — one that transmits not only sight and sound, but also touch, texture, and even smell. Imagine shopping online and feeling the fabric before buying, or experiencing a concert as if you were physically there.
Why it matters:
The leap from 5G to 6G isn’t just about “faster Netflix.” It’s about building the backbone for immersive, AI-driven digital life. With speed, latency, and intelligence working together, next generation wireless connectivity will redefine communication, entertainment, healthcare, and industry.
The future of mobile networks with 6G
Mobile networks have always been about more than just phones. Each generation expanded the boundaries of what was possible, and with 6G technology, we’re stepping into a future where connectivity becomes as invisible — and essential — as electricity. The future of mobile networks will reshape healthcare, education, industry, entertainment, and urban life in ways that feel straight out of science fiction.
Healthcare: medicine without borders
With ultra-low latency and AI-powered data exchange, 6G could make healthcare truly borderless. Doctors could perform delicate surgeries using robotic systems while guiding them in real time from across the world. Wearables could monitor patient health continuously, sending instant alerts to medical teams. Rural communities that currently lack specialists could get access to top-tier healthcare through remote telepresence.
Imagine a world where medical checkups happen in holographic clinics, with doctors who appear right in your living room. That’s the kind of transformation 6G can enable.
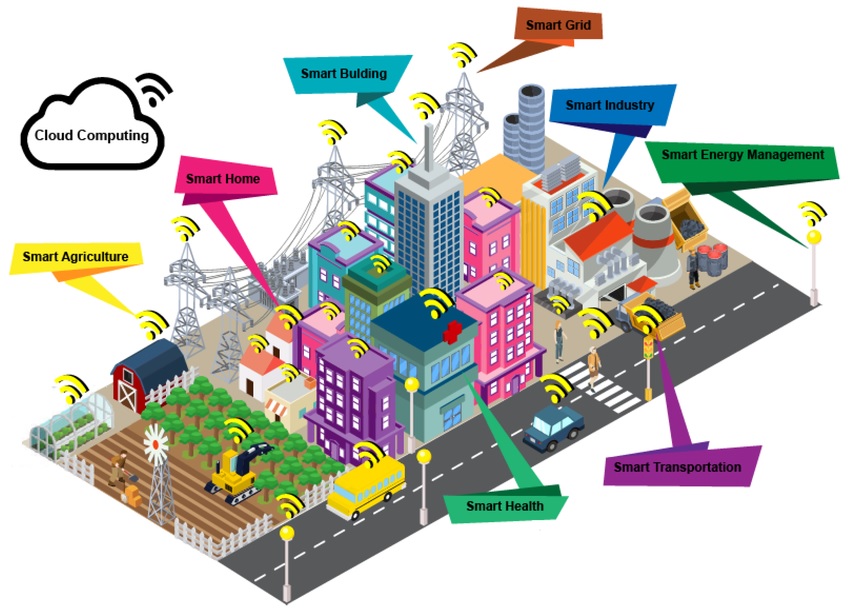
Smart cities: the urban brain
Today’s cities are connected, but often in fragmented ways — traffic systems here, utility sensors there. 6G could bring it all together into a single, real-time digital ecosystem. Traffic lights could communicate with self-driving cars to prevent collisions. Energy grids could balance loads instantly. Emergency services could get live situational awareness via drones and connected sensors.
In other words, cities could become living, thinking organisms that respond dynamically to the needs of their residents.
Education: holograms over homework
The pandemic taught us the limits of video calls for learning. With 6G, students could step into immersive holographic classrooms where teachers appear as lifelike 3D projections. Students could conduct virtual science experiments together in real time, or explore ancient civilizations as if they were walking through them.
For remote and underserved regions, this could be a game-changer — offering world-class education without physical barriers.
Entertainment: immersion without limits
From Netflix to TikTok, entertainment has been defined by bandwidth. 6G will push this to another level. Imagine attending a concert where your favorite artist appears as a hologram in your living room. Or watching a football match not from the sidelines, but actually walking onto the pitch virtually.
Gamers will see the biggest transformation. Cloud gaming powered by 6G means no downloads, no lag — just instant, fully immersive play in ultra-realistic virtual environments.
Industry: the autonomous revolution
Manufacturing and logistics will benefit massively from 6G. With billions of sensors communicating simultaneously, factories can run autonomously, with machines making real-time adjustments. Delivery drones and autonomous trucks could coordinate with traffic systems for efficient routing. This isn’t just about convenience — it’s about billions in saved costs and reduced human error.
Why it matters:
The future of mobile networks will not just connect people but connect everything — from machines and vehicles to cities and even our senses. With next generation wireless connectivity, the world becomes more responsive, immersive, and intelligent, opening up possibilities we’ve only dreamed of.
The global race for 6G leadership
While most of us are still waiting for 5G to roll out everywhere, governments and telecom giants are already gearing up for the 6G arms race. Why? Because whichever country or company leads in 6G will set the global standards, control key patents, and shape the future digital economy.
China: racing ahead
China has made no secret of its ambitions. It launched one of the world’s first 6G test satellites in 2020 and is heavily investing in terahertz research. Chinese telecom firms like Huawei and ZTE are partnering with government programs to dominate the standards-setting process.
South Korea and Japan: innovation hubs
South Korea, a leader in 5G, aims to launch 6G as early as 2028. Samsung and LG are already running trials and publishing white papers on 6G’s capabilities. Japan, meanwhile, has pledged billions in funding to ensure it remains at the forefront, with companies like NTT Docomo pushing research partnerships.
The United States: private-sector power
The U.S. may have been slower on 5G rollout, but American companies are determined not to fall behind on 6G. Firms like Qualcomm, Intel, and AT&T are investing heavily, while the U.S. government has launched the Next G Alliance, a coalition designed to lead North America into the 6G era.
Europe: collaborative approach
The EU is taking a coordinated approach with its Hexa-X project, involving Nokia, Ericsson, and other European partners. The focus is not just on speed but also on sustainability and inclusivity.
Why it matters:
The race for 6G leadership is about much more than faster phones. It’s about who controls the backbone of global digital infrastructure for decades to come. Just like oil defined power in the 20th century, connectivity will define power in the 21st.
When will 6G launch?
The big question on everyone’s mind: when will 6G launch? While it sounds futuristic, the roadmap is already in motion. Unlike app updates, mobile generations take years of research, standardization, and infrastructure building before they ever reach your phone.
Here’s what the timeline looks like:
2020–2025: research phase
Right now, universities, telecom firms, and governments are running early research trials. This includes terahertz spectrum testing, AI-native network design, and prototypes of new hardware. Companies like Samsung, Huawei, Nokia, and Ericsson have already published white papers on what 6G might look like.
2025–2028: standardization
Before 6G can launch, global standards must be agreed upon. This work will be led by organizations like the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) and the ITU (International Telecommunication Union). These standards define everything from spectrum allocation to security requirements. Expect heated debates as countries push for influence.
2028–2030: pilot testing
This is when we’ll see experimental 6G networks in select cities, much like the early 5G testbeds in Seoul, Tokyo, and New York. These pilots will iron out technical challenges and give industries a chance to adapt.
Early 2030s: commercial rollout
If everything stays on track, early 2030s will mark the first consumer-ready 6G networks. As with 5G, adoption will be uneven at first, concentrated in advanced economies before spreading globally.
What this means for users:
Don’t expect to see “6G” pop up on your phone anytime soon. But within a decade, the next generation wireless connectivity could be powering your smart home, workplace, and city. For now, 5G Advanced will bridge the gap, preparing networks and devices for the leap.
5G Advanced vs 6G: the stepping stone to the future
Before we get to the 6G era, there’s an important pit stop: 5G Advanced. Think of it as 5G’s “supercharged upgrade” — a halfway point between today’s networks and tomorrow’s terahertz-powered future.
What is 5G Advanced?
5G Advanced is an evolution of existing 5G networks, set to roll out globally between 2025 and 2028. It enhances the core of 5G with features like:
- Better energy efficiency: Smarter resource allocation reduces power consumption across networks.
- AI integration: AI will play a bigger role in traffic management and predictive network optimization.
- Enhanced IoT capabilities: Supporting more devices with improved reliability.
- Improved coverage: Filling gaps in rural and remote areas that current 5G struggles to reach.
How it differs from 6G
While 5G Advanced improves today’s networks, 6G represents a complete redesign:
- 5G Advanced: Faster, greener, and smarter than current 5G, but still limited to existing spectrum ranges (sub-6 GHz and millimeter waves).
- 6G: Jumps to terahertz spectrum, enabling speeds up to 1 Tbps. It’s AI-native, not just AI-enhanced, and it integrates land, air, and space networks.
Why this matters for users
5G Advanced will act as a bridge, giving industries and consumers a taste of what’s possible while laying the groundwork for 6G. It ensures a smoother transition so that when 6G arrives in the early 2030s, the world will be ready.
Analogy: If 5G is the sports car that revolutionized the highway, and 6G is the spaceship ready to take us to new galaxies, then 5G Advanced is the turbo upgrade that prepares us for lift-off.
6G applications in daily life
It’s one thing to talk about 1 Tbps speeds and AI-native networks, but what does 6G actually mean for you and me? Here’s a look at how 6G applications in daily life could transform everything from entertainment to healthcare.
1. Home entertainment: beyond streaming
We thought Netflix and 4K streaming were peak luxury. With 6G, we’ll move past watching to experiencing. Imagine your favorite band giving a holographic concert in your living room, or streaming a blockbuster film in 16K quality without downloading a single gigabyte.
Gamers will be the biggest winners. Cloud gaming over 6G means no downloads, no updates, no lag — just instant access to immersive, ultra-realistic worlds streamed directly to VR or AR headsets.
2. Holographic communication
Video calls are great, but what if your friend could appear in your kitchen as a life-sized hologram? With 6G’s microsecond latency, holographic communication will feel natural, creating the sense of truly “being there” even across continents. This could redefine remote work, social interactions, and even how families stay connected.
3. Healthcare: real-time wellness
Your smartwatch today counts steps and maybe measures your heart rate. A 6G-powered wearable could continuously monitor your body, detect irregularities, and alert your doctor instantly. Doctors could run holographic checkups from afar, and emergency responses could happen within seconds thanks to real-time data sharing.
Rural areas, where healthcare access is often limited, could see massive improvements with telepresence medicine — specialists “visiting” patients holographically.
4. Smart homes that anticipate your needs
Forget voice commands — your home could predict what you need. The fridge might automatically order groceries when you’re running low. Your thermostat could sync with weather forecasts and your daily schedule to keep things just right. Thanks to AI-native networks, devices would work together seamlessly, without the annoying lag or glitches we see today.
5. Shopping in 3D
Online shopping could feel like stepping into a mall. With holographic projection, you’d try on clothes virtually, feel textures via tactile internet, and preview furniture in your living room before buying. For retailers, this means fewer returns; for consumers, it’s shopping reimagined.
6. Travel and transportation
Autonomous cars will benefit enormously from 6G. Vehicles could communicate with traffic lights, drones, and each other in real time, practically eliminating accidents caused by delays. Public transport could be optimized minute-by-minute based on live passenger flow data.
7. Education without borders
Imagine students in rural areas attending a physics class where the teacher appears as a hologram. They could conduct virtual experiments, walk through 3D models of the solar system, or explore ancient ruins in an immersive history lesson. Education powered by 6G could democratize access to world-class learning.
Why this matters:
6G applications won’t just change how we use technology — they’ll change how we experience the world. From shopping and gaming to healthcare and work, next generation wireless connectivity will make the digital and physical worlds merge seamlessly.
Challenges and sustainability issues
For all its promises, 6G technology won’t be an overnight success story. Building a global, AI-powered, terahertz-driven network comes with challenges — technical, economic, environmental, and ethical. Let’s break down the biggest hurdles.
1. Infrastructure costs
Deploying 6G isn’t as simple as flipping a switch on existing towers. Because terahertz waves travel shorter distances and are easily blocked by walls, 6G will need dense networks of small cells, repeaters, and satellites. That means billions in new infrastructure investments — a cost that may delay rollout in less wealthy regions.
2. Energy consumption
One of the elephants in the room is power demand. Terahertz frequencies require enormous energy to operate, raising concerns about sustainability. Telecom providers will need to pair 6G expansion with green technologies like renewable energy and AI-driven efficiency tools. Otherwise, the environmental footprint could be huge.
3. Cybersecurity and privacy
With billions of devices — from cars to pacemakers — connected at once, the attack surface for hackers grows exponentially. AI-powered networks can help defend against threats, but new security standards will be critical. Governments, businesses, and regulators must collaborate to protect data, privacy, and national security.
4. Global inequality
Like 5G, 6G risks widening the digital divide. Wealthy nations may see early adoption, while developing regions lag behind. This could deepen inequalities in education, healthcare, and economic opportunity. A fair, inclusive rollout must be a top priority.
5. Health and safety concerns
Every new generation of wireless technology faces questions about health impacts. Current research shows no evidence of harm from high-frequency waves, but 6G’s terahertz spectrum will undergo rigorous testing before mass deployment. Transparency will be key to building public trust.
The bottom line:
6G has the potential to revolutionize life, but only if it’s sustainable, secure, and inclusive. Without addressing these challenges, we risk building a network that benefits only a select few while draining global resources. With the right balance, however, 6G could be both transformative and responsible.
The playful side of 6G: what life could look like
Technology articles often focus on numbers and specs, but 6G technology has a playful side too. Imagine waking up in a world where connectivity feels like magic.
You roll out of bed, and your smart mirror shows you today’s outfit — not just in a photo, but in a holographic projection you can virtually “try on.” On the way to work, your self-driving car chats with traffic lights and delivery drones, plotting the fastest route without a single red light.
At lunch, you “meet” a friend in Paris — holographically. You’re sipping coffee in London, they’re at a café near the Eiffel Tower, yet it feels like you’re at the same table. Later, your kids attend a history lesson where they walk through the pyramids in VR, guided by a holographic teacher.
By evening, your living room transforms into a concert arena. Your favorite artist appears as a hologram, performing live, while your AI assistant syncs the lighting and sound perfectly to match the beat.
It sounds like sci-fi — but with next generation wireless connectivity, this could be just another Tuesday.
FAQs about 6G technology
Q1: How fast is 6G compared to 5G?
6G is projected to reach speeds of up to 1 terabit per second (Tbps), nearly 100 times faster than 5G’s peak of around 10 gigabits per second (Gbps). That means tasks like downloading a full-length 8K movie could take less than a second.
Q2: When will 6G be available to consumers?
Most experts predict early 2030s for commercial rollout. Before then, we’ll see pilot projects in leading tech hubs like South Korea, Japan, China, and the U.S. Starting around 2025, 5G Advanced will serve as the stepping stone.
Q3: What is the difference between 5G Advanced and 6G?
- 5G Advanced: An upgrade to current 5G networks, with better AI integration, improved IoT support, and greener infrastructure.
- 6G: A whole new era using the terahertz spectrum, AI-native design, and speeds up to 1 Tbps.
Q4: What are some 6G applications in daily life?
6G will enable holographic communication, immersive education, smart healthcare, autonomous transport, and AI-driven homes. It will make digital interactions feel as natural as face-to-face experiences.
Q5: Will 6G replace Wi-Fi?
Not entirely. Wi-Fi will continue to evolve alongside mobile networks. But with 6G’s ultra-fast, low-latency capabilities, many tasks traditionally reliant on Wi-Fi could shift to mobile connectivity.