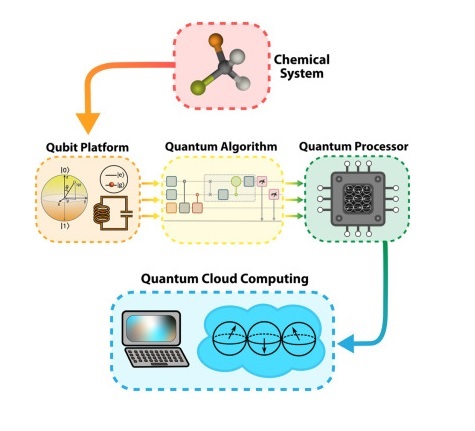
Quantum computing sounds like something straight out of a sci-fi movie – all glowing circuits and mysterious math. But at its core, it’s simply the next big leap in how computers process information. Traditional computers rely on bits, which can be either 0 or 1. Quantum computers, on the other hand, use qubits – which can be 0, 1, or both at the same time. This magical middle ground is called superposition, and it’s what gives quantum computing its mind-bending power.
Imagine flipping a coin. A traditional computer only sees heads or tails. A quantum computer can work with both states simultaneously, giving it a serious advantage in solving complex problems. Add another trick called entanglement – where qubits share information instantly even when far apart – and suddenly, these machines can tackle calculations that would take classical computers centuries to finish.
In short, quantum computing isn’t about making your laptop faster; it’s about creating an entirely new way of computing. It’s like comparing a bicycle to a jet plane – both move forward, but one clearly redefines the journey.
And while the technology is still developing, 2025 marks a turning point. Quantum technology companies are moving from theoretical experiments to real-world prototypes. Giants like IBM, Google, and startups like Rigetti and IonQ are racing to make quantum computing accessible, scalable, and – eventually – consumer-friendly.
Quantum technology advancements in 2025
If 2024 was about quantum computing proving its potential, 2025 is the year it starts to prove its purpose. The industry is shifting from lab tests to real-world performance, and quantum technology companies are racing to achieve quantum advantage – the moment when a quantum computer outperforms classical machines at a meaningful task.
So, what’s new this year? Several things are driving this next leap forward:
- Better qubit stability:
One of the biggest hurdles for quantum computing has been keeping qubits stable long enough to complete calculations. In 2025, improved error correction methods and materials like superconducting circuits and trapped ions are dramatically extending qubit coherence times – meaning fewer crashes and more accurate results.
- Cloud-based quantum access:
Companies like IBM, Amazon Braket, and Microsoft Azure Quantum are making quantum computing available through the cloud. Instead of needing a massive cryogenic lab, researchers and developers can now rent quantum computing power online. This “quantum-as-a-service” model makes the technology far more accessible to startups, universities, and even hobbyists.
- Quantum chips go hybrid:
Quantum and classical processors are beginning to team up. Hybrid computing models allow traditional CPUs to handle basic logic while quantum cores tackle the heavy number crunching. This integration is key for practical applications, especially in artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and data analytics.
- Government and private investment:
The global race for quantum dominance has never been hotter. The U.S., U.K., and China have all increased national funding for quantum research, while venture capital firms are pouring billions into startups specializing in quantum hardware, software, and materials science.
These advancements are bringing quantum computing out of the shadows and into practical reality. It’s no longer just a research experiment; it’s becoming a powerful tool that could soon rival – and redefine – modern computing.
Quantum computing applications and real-world use cases
Now that quantum computing has matured beyond the lab, it’s finding its footing in industries that crave speed, precision, and problem-solving power. In 2025, we’re beginning to see quantum technology move from theoretical discussions into real-world use cases that directly or indirectly touch consumer life.
Let’s break down where quantum computing is already making an impact – and where it’s headed next.
1. Drug discovery and healthcare
Traditional drug discovery can take years of trial and error. Quantum computing changes that by simulating molecular structures and chemical reactions at unprecedented speeds. Instead of running thousands of physical experiments, pharmaceutical companies can now model how molecules behave at the quantum level. In 2025, companies like Biogen and Roche are experimenting with quantum-powered simulations to accelerate treatments for diseases like Alzheimer’s and cancer.
2. Cybersecurity and encryption
Ironically, the same technology that can break encryption could also reinvent it. Quantum computers can theoretically crack today’s most secure cryptographic systems – but researchers are already working on post-quantum cryptography, a new generation of encryption designed to be quantum-proof. For consumers, this means safer online transactions, more secure communication apps, and banking systems fortified against future cyber threats.
3. Artificial intelligence and machine learning
Quantum computing and AI integration is one of the most exciting tech mashups of 2025. Quantum algorithms can process and analyze massive datasets more efficiently than classical systems. Imagine training AI models in hours instead of days – that’s the promise quantum brings. Google and NVIDIA are experimenting with quantum-enhanced AI to refine pattern recognition, optimize logistics, and even improve generative AI outputs.
4. Climate modeling and sustainability
Quantum computing’s problem-solving prowess could help tackle one of humanity’s biggest challenges: climate change. Quantum models can simulate complex atmospheric systems and energy materials, helping scientists design more efficient batteries, optimize renewable energy grids, and reduce waste in supply chains.
5. Finance and risk analysis
Financial institutions are early adopters of quantum computing for portfolio optimization, fraud detection, and real-time market prediction. In 2025, major banks like JPMorgan Chase and Goldman Sachs are piloting quantum models to simulate millions of scenarios simultaneously – helping minimize risk and maximize returns faster than ever.
Quantum computing applications may sound like high-tech wizardry, but the results are already showing up in places consumers recognize – from smarter AI assistants to more secure cloud services. As the technology matures, the line between “quantum research” and “quantum reality” continues to blur.
Benefits of quantum computing for everyday consumers
At first glance, quantum computing might seem like something only scientists and tech giants would care about. But just as the internet and smartphones eventually transformed daily life, the quantum revolution will quietly reshape how consumers interact with technology – even if they don’t notice it happening.
Let’s explore what the benefits of quantum computing could mean for the average person in 2025 and beyond.
1. Faster, smarter digital services
Quantum computers can process data at speeds traditional systems can’t match. This means cloud services, AI assistants, and even social platforms can deliver faster, more accurate results. Imagine your voice assistant understanding context instantly, or your cloud storage predicting and organizing your files intelligently. Quantum acceleration could make every digital experience smoother and smarter.
2. Stronger online security
Quantum encryption is paving the way for ultra-secure communication. Your future online banking sessions and email exchanges could be protected by quantum-safe encryption keys – uncrackable even by the most powerful classical computers. As more companies adopt post-quantum cryptography, consumers gain peace of mind knowing their private data is safer than ever.
3. Smarter healthcare and personalized medicine
Quantum computing could drastically improve how your health data is analyzed. In the coming years, wearable devices and medical AI could use quantum algorithms to detect patterns invisible to classical computers – predicting potential health risks before they become serious. Personalized medicine, powered by quantum insights, could become a mainstream reality.
4. More efficient energy and sustainability solutions
From electric cars to smart homes, energy efficiency is set to benefit massively. Quantum modeling helps design better battery materials and optimize power consumption at a granular level. The result? Devices that last longer, charge faster, and consume less energy – good for both your wallet and the planet.
5. Enhanced AI and smarter automation
Everyday technologies like chatbots, recommendation systems, and self-driving cars stand to benefit from quantum-AI integration. By processing more variables at once, these systems can make decisions faster and more accurately, improving experiences across entertainment, e-commerce, and travel.
6. Better financial decisions
As financial institutions embrace quantum-powered simulations, consumers may soon see smarter loan approvals, more accurate credit scoring, and investment tools that adapt to real-time data. Think of it as AI-powered finance – on quantum steroids.
Quantum computing might still feel distant, but the benefits are already trickling into the tools and services people use daily. By 2025, it’s not about if consumers will feel its impact – but how soon and how deeply it will transform their digital experiences.
Quantum computing and AI integration: the next tech superpower
When two of the most powerful technologies – artificial intelligence and quantum computing – join forces, the result is nothing short of revolutionary. This fusion, often dubbed Quantum AI, is already redefining how machines learn, adapt, and think. By 2025, the conversation isn’t just about faster computing – it’s about creating smarter, more capable systems that can solve problems we once thought were impossible.
Why AI needs quantum computing
AI today is limited by classical hardware. Training large models, such as those powering natural language processing or image recognition, consumes vast amounts of energy and time. Quantum computing changes that equation. With qubits working in parallel, quantum processors can analyze massive datasets and test multiple solutions simultaneously – cutting training time dramatically.
Think of it like a chef who can taste every variation of a recipe at once before choosing the perfect version. That’s the advantage Quantum AI brings to the table.
Real-world examples in 2025
- Drug discovery acceleration: AI models trained on quantum data are helping scientists predict molecular interactions faster, leading to rapid vaccine and drug development.
- Financial forecasting: Banks are experimenting with quantum-enhanced AI for near-instant market simulations, helping traders make smarter investment decisions in real time.
- Smart manufacturing: Quantum AI systems optimize logistics, supply chains, and predictive maintenance, reducing waste and downtime.
- Generative AI improvements: Quantum algorithms could supercharge the creative side of AI – from generating realistic video content to simulating virtual worlds with stunning accuracy.
Ethical and practical considerations
Of course, combining AI and quantum power raises big questions. Who controls these powerful systems? How do we prevent misuse? And what happens when machines can outpace human comprehension in problem-solving? As 2025 unfolds, tech companies and regulators alike are drafting frameworks to ensure ethical, transparent use of Quantum AI.
But there’s no denying it – quantum computing and AI integration will define the next decade of technological innovation. From smarter assistants to predictive medicine, the fusion of quantum power and artificial intelligence is becoming the digital brain behind a smarter planet.
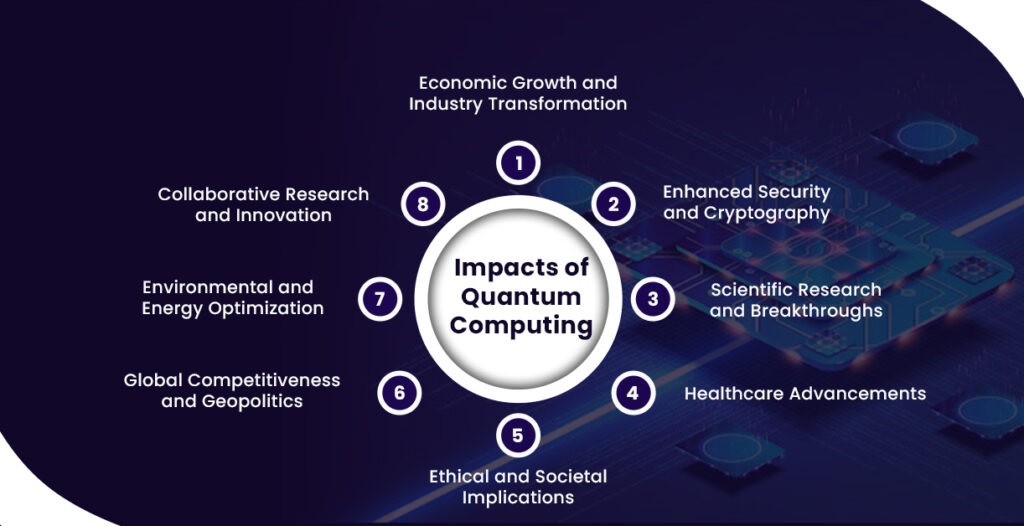
Quantum computing future outlook: what’s next for consumers and industries
If 2025 is the dawn of practical quantum computing, the next decade will be its sunrise – bright, transformative, and impossible to ignore. Quantum computing’s journey from research labs to consumer tech is happening faster than most predicted, and its future outlook points toward a world where these systems quietly power everything from finance to entertainment.
1. Quantum computing goes mainstream
Within the next five years, we can expect the first wave of consumer-facing quantum applications. This doesn’t mean people will have quantum chips in their laptops, but cloud services and AI-driven platforms will increasingly rely on quantum backends for optimization and analysis. You might not “see” quantum computing, but you’ll definitely feel it – in faster streaming, more accurate recommendations, and smoother online experiences.
2. Quantum internet and ultra-secure communication
One of the most anticipated developments is the rise of the quantum internet. By using quantum entanglement, data could be transmitted securely and instantly over vast distances. China, the U.S., and Europe are all testing prototypes of quantum communication networks that promise zero risk of interception. For consumers, this could eventually mean hack-proof messaging, banking, and online voting.
3. Expanding ecosystem of quantum technology companies
2025 has already seen a surge in startups focused on specialized areas like quantum sensors, quantum networking, and quantum software platforms. These smaller players complement the big names like Google, IBM, and Intel, creating a thriving ecosystem that accelerates innovation. Expect more partnerships between academia, governments, and private enterprises – each racing to commercialize quantum breakthroughs.
4. Democratization through quantum-as-a-service
Just like cloud computing changed how businesses accessed infrastructure, quantum-as-a-service (QaaS) will democratize access to powerful quantum processors. Developers, researchers, and even advanced consumers will be able to tap into quantum systems remotely to run simulations, optimize algorithms, or test ideas that were once impossible on classical machines.
5. The ethical frontier
With great power comes, well, a quantum-sized set of responsibilities. As quantum systems grow in capability, society will need to address concerns around privacy, data control, and the potential misuse of ultra-powerful computing. The same technology that can break encryption could, in the wrong hands, compromise global security. That’s why regulators are racing to set ethical boundaries before quantum computing becomes as ubiquitous as AI.
The takeaway
Quantum computing’s future outlook is clear: it will quietly weave itself into the digital fabric of everyday life. Consumers may never see the quantum chip itself, but they’ll benefit from faster AI, safer communications, smarter products, and greener solutions. In short, quantum computing won’t just make technology better – it will make it smarter, fairer, and faster for everyone.
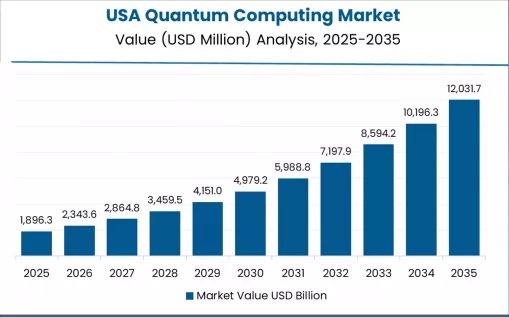
Conclusion: the quantum leap toward a smarter tomorrow
Quantum computing in 2025 isn’t just a buzzword – it’s a genuine technological revolution unfolding in real time. While the average consumer might not interact directly with a quantum computer, its ripple effects are already reshaping how we live, work, and connect.
From boosting artificial intelligence and advancing medical research to making online security nearly unbreakable, quantum technology is fast becoming the invisible engine of progress. What once required decades of trial and error can now be simulated in moments. The impossible is becoming routine.
The beauty of this evolution lies in its subtlety – consumers won’t need to understand qubits or entanglement to enjoy the results. Just as no one needs to know how Wi-Fi or GPS truly works to benefit from them, quantum computing will seamlessly blend into everyday life, powering smarter devices, safer networks, and faster decisions across industries.
As we stand on the edge of this quantum era, one thing is certain: the next ten years will redefine what “smart technology” means. The question isn’t whether quantum computing will change the world – it’s how deeply it will reshape everything we know about it.

FAQs: quantum computing 2025 and what it means for you
1. What is quantum computing in simple terms?
Quantum computing is a new way of processing information that uses qubits instead of traditional bits. Unlike regular bits, which can only be 0 or 1, qubits can represent both at once thanks to superposition. This allows quantum computers to solve complex problems much faster than classical computers.
2. How is quantum computing different from traditional computing?
Traditional computers use binary logic to process tasks step by step, while quantum computers can process multiple possibilities simultaneously. This makes them ideal for tackling massive computations such as drug discovery, financial modeling, and advanced AI training.
3. Are there any real-world applications of quantum computing in 2025?
Yes, several! In 2025, quantum computing applications are already being explored in drug discovery, cybersecurity, AI optimization, financial risk management, and even climate modeling. Tech giants and startups alike are integrating quantum algorithms to enhance performance and precision in various sectors.
4. How will quantum computing benefit everyday consumers?
Consumers will experience the benefits indirectly – through faster AI assistants, more secure banking systems, improved healthcare analytics, and optimized energy solutions. You may not own a quantum device, but the services you use daily will increasingly rely on quantum power.
5. Is quantum computing safe?
Quantum computing itself is not unsafe, but it does pose challenges for current encryption methods. That’s why researchers are developing post-quantum cryptography, designed to protect data even in a quantum-powered world. Once adopted globally, this will make digital systems more secure than ever.
6. Which companies are leading the quantum computing race?
Some of the most active quantum technology companies include IBM, Google, Intel, Microsoft, Rigetti Computing, and IonQ. These companies are driving innovation in both hardware and software, bringing quantum technology closer to commercial reality.
7. Will quantum computers replace regular computers?
Not anytime soon. Quantum computers excel at solving specific types of complex problems but are not designed for everyday tasks like browsing or word processing. Instead, they’ll work alongside classical systems in hybrid setups, enhancing performance where it matters most.