If traditional automation is like a calculator, AI agents are more like a junior employee who actually understands the task, figures out the next step, and gets on with it without being asked every five minutes.
Businesses are moving fast from basic scripts and rule-based bots to intelligent systems that can think, decide, and act on their own. That shift is driven by autonomous AI agents, tools designed to handle complex workflows without constant human input. From scheduling meetings to managing data pipelines and customer support, AI workflow automation is quietly replacing manual processes that once ate up hours of human time.
Many autonomous AI agents rely on architectural choices similar to those discussed in cloud AI vs edge AI, where decisions about latency, control, and data access shape how intelligent systems can operate on their own.
In this guide, AI agents explained clearly and without hype, we’ll break down what they are, how they work, why they matter, and how they’re reshaping modern work. Whether you’re curious, technical, or thinking about using AI agents for business, this article will give you a clear picture of what’s happening and what’s coming next.
What are AI agents?
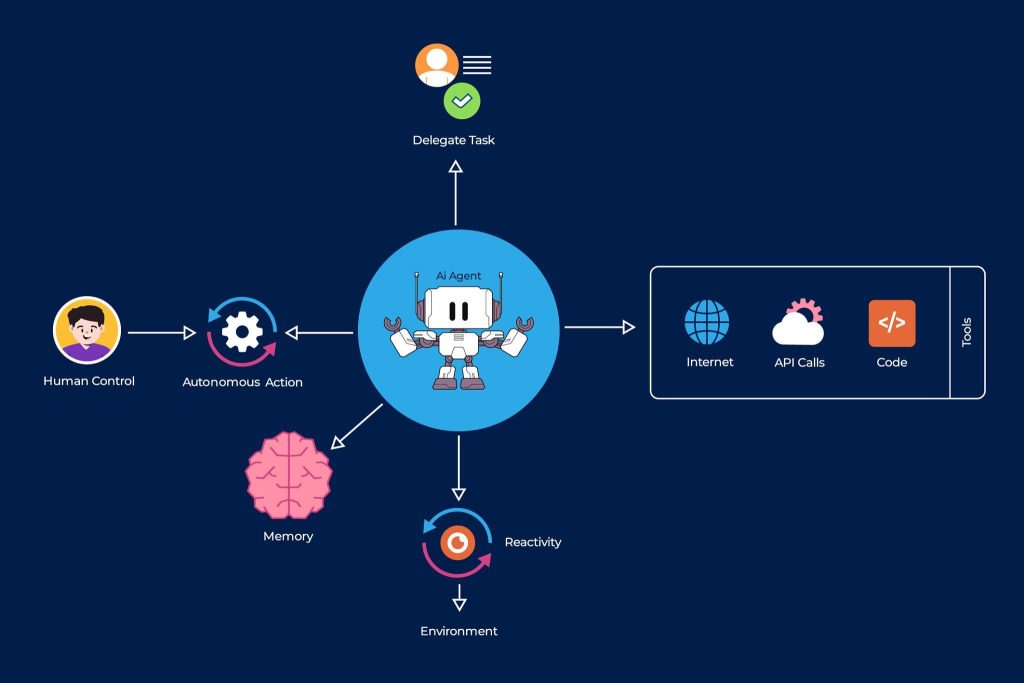
At their core, AI agents are software systems designed to perceive information, make decisions, and take action to achieve specific goals. Unlike simple automation tools that follow fixed rules, AI agents can adapt based on context, feedback, and changing conditions.
Think of them as task-oriented AI workers. You give them an objective, access to tools or data, and boundaries to operate within. From there, they decide how to complete the task step by step.
Key characteristics of AI agents
AI agents typically have a few defining traits that set them apart from traditional automation:
- They operate with a goal rather than a single instruction
- They can decide what action to take next
- They use tools such as APIs, databases, or apps
- They can run continuously or trigger themselves when conditions change
This is why many people searching for what AI agents are quickly realize they’re not just smarter chatbots. They’re closer to autonomous systems designed to get work done.
Why AI agents are different from basic automation
Traditional automation works well for predictable tasks. If X happens, do Y. AI agents go further by handling ambiguity. If something unexpected happens, they reassess, choose a new path, and continue working.
That flexibility is what makes autonomous AI agents so powerful in real-world business environments where perfect data and predictable scenarios rarely exist.
AI agents vs traditional automation and chatbots
One of the biggest sources of confusion around this topic is how AI agents differ from the tools businesses already use. Many people assume AI agents are just smarter chatbots or slightly upgraded automation scripts. In reality, they represent a completely different way of thinking about work.
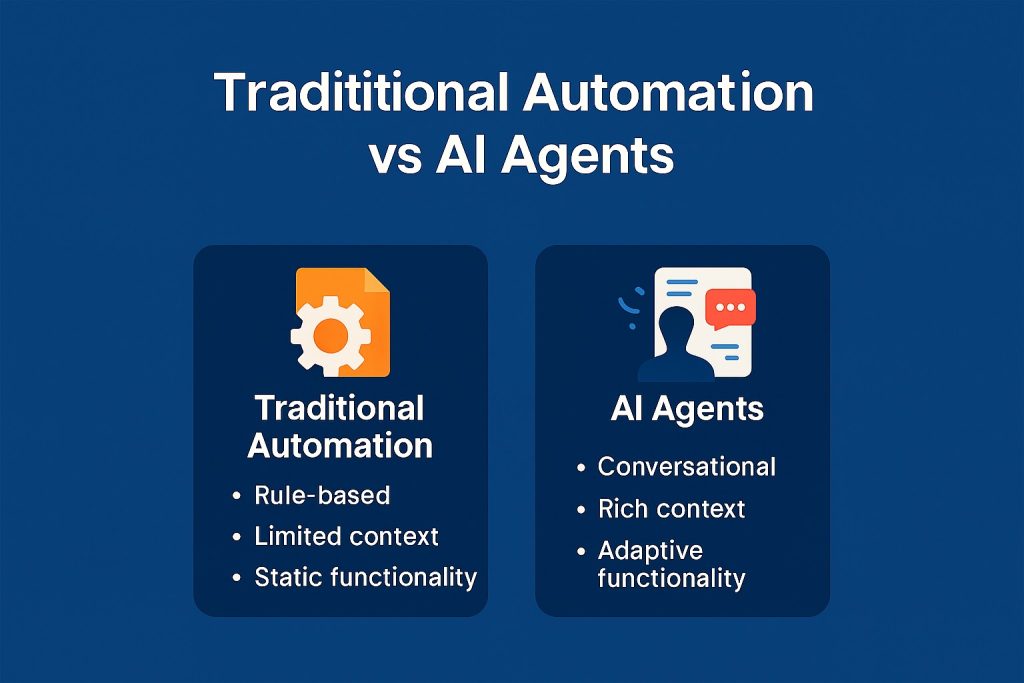
Traditional automation: fast but fragile
Traditional automation tools are excellent at repetitive, clearly defined tasks. Think spreadsheet macros, email rules, or basic workflow automation platforms. They work like a checklist:
- If a form is submitted, send an email
- If a value changes, update a database
- If a condition is met, trigger a task
This approach works well until something changes. New data formats, unexpected inputs, or missing information can cause the whole workflow to break. That’s why many companies end up with dozens of brittle automations that require constant maintenance.
Chatbots: conversational but limited
Chatbots added a layer of intelligence, mainly in how users interact with systems. They can answer questions, guide users, and even perform simple actions. However, most chatbots are reactive. They wait for a prompt, respond, and then stop.
Even advanced chatbots usually can’t:
- Plan multi-step workflows
- Decide when to act on their own
- Use multiple tools without human guidance
- Monitor long-running processes
This is where the comparison of AI agents vs chatbots becomes important. Chatbots talk. AI agents do.
AI agents: goal-driven and proactive
AI agents are built around objectives rather than conversations or rules. You define the goal, provide access to tools, and the agent figures out how to reach that outcome.
For example, instead of telling a system to “send a report every Friday,” you tell an AI agent to “keep stakeholders informed about performance.” The agent decides what data to pull, when to send updates, and how to adjust if something changes.
This shift enables true AI workflow automation, where systems don’t just execute steps but manage entire processes end to end.
A simple comparison
To make it clearer, here’s how the three approaches differ in practice:
- Traditional automation follows fixed rules
- Chatbots respond to prompts and questions
- AI agents plan, decide, and act autonomously
That planning and decision-making layer is what turns automation into something much closer to digital labor.
How autonomous AI agents actually work
To really understand why autonomous AI agents are replacing manual workflows, it helps to look under the hood. While the technology can feel almost magical, the core idea is surprisingly structured.
Most AI agents follow a repeating loop: observe, decide, act, and learn. This loop allows them to operate continuously rather than responding once and stopping.
Step 1: Understanding the goal
Every AI agent starts with a goal. This might be simple, like organizing incoming support tickets, or complex, like managing an entire marketing campaign.
Unlike traditional automation, the goal is not a fixed script. It’s a desired outcome. The agent interprets that goal and breaks it down into smaller tasks it needs to complete.
Step 2: Perception and data intake
AI agents constantly collect information from their environment. This could include:
- Emails, documents, or chat messages
- CRM or database records
- Website analytics or system logs
- API responses from external tools
This perception step allows agents to stay aware of what’s happening in real time, which is essential for AI agents for business operating in fast-moving environments.
Step 3: Planning and reasoning
This is where agentic AI workflows really shine. The agent decides what to do next based on its goal and current context. It may plan multiple steps ahead, evaluate different options, and choose the most efficient path forward.
If something goes wrong, the agent can adjust its plan instead of failing outright. This flexibility is one of the biggest advantages of AI automation tools built around agents rather than rules.
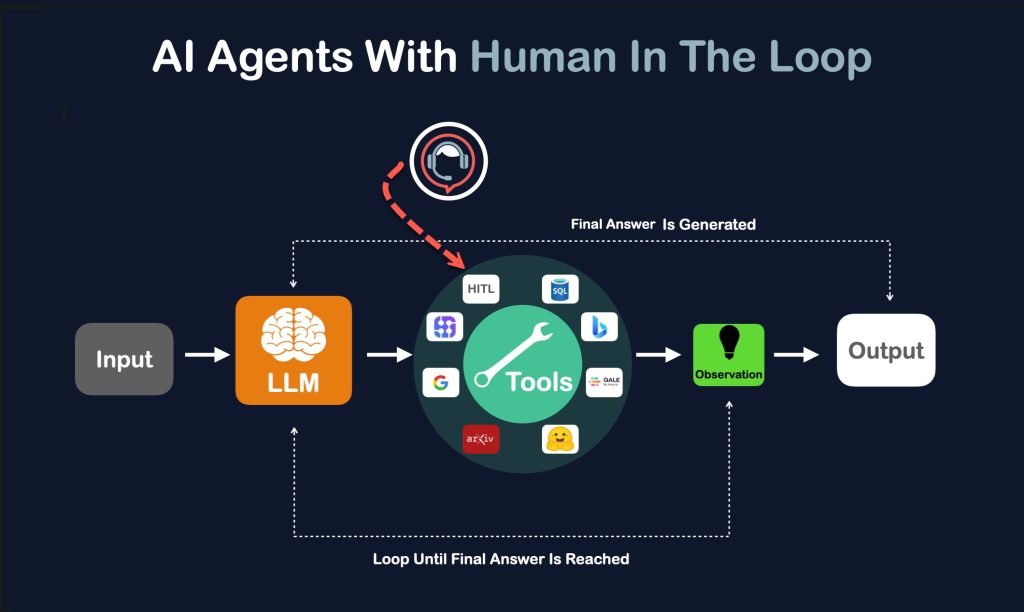
Step 4: Taking action using tools
Once a decision is made, the agent acts. Actions might include:
- Sending emails or messages
- Updating spreadsheets or databases
- Calling APIs or triggering software actions
- Creating documents or reports
In many cases, agents can chain actions together across multiple platforms, which is why they’re so effective at replacing manual workflows that jump between tools.
Step 5: Feedback and improvement
Good AI agents don’t just act once. They monitor the results of their actions and use that feedback to improve future decisions. Over time, this leads to better outcomes with less human oversight.
This continuous loop is what makes autonomous AI agents feel less like software and more like digital coworkers that learn how your business operates.
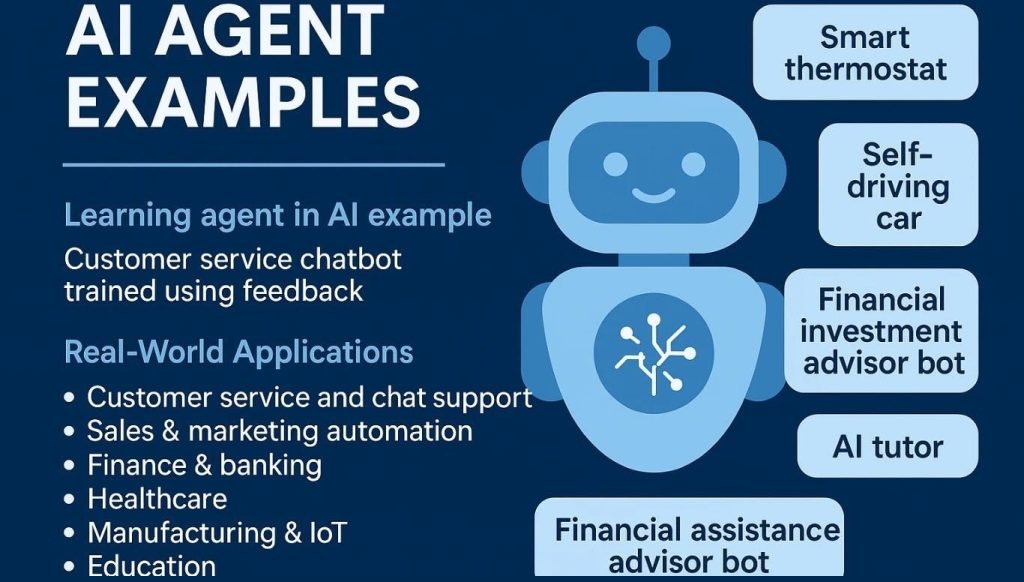
Real-world AI agent examples and use cases
Many of these use cases build on the same foundations as modern AI productivity tools, but extend them further by allowing systems to plan, act, and adapt without constant human input.
Understanding how AI agents work is useful, but seeing them in action is where everything clicks. Across industries, companies are already using AI agents to replace manual workflows that once required constant human attention.
Below are some of the most common and impactful AI agent examples being used today.
AI agents for customer support
In customer support, AI agents go far beyond answering FAQs. They can:
- Monitor incoming tickets across channels
- Categorize and prioritize issues automatically
- Pull customer history from CRMs
- Draft responses or resolve issues directly
- Escalate complex cases to humans when needed
Instead of reacting to every message, support teams oversee agents that handle routine issues independently. This reduces response times while freeing humans to focus on edge cases and high-value interactions.
AI agents in marketing and content workflows
Marketing teams are using AI agents to manage tasks that were once highly manual:
- Researching topics and keywords
- Monitoring campaign performance
- Generating reports and insights
- Adjusting ad spend based on performance signals
These agents don’t just generate content. They monitor outcomes and adapt strategies, making them far more powerful than one-off AI tools.
AI agents for sales and lead management
Sales workflows are another area where AI agents for business deliver immediate value. Agents can:
- Track new leads from multiple sources
- Enrich lead data using external tools
- Score leads based on behavior
- Schedule follow-ups automatically
Instead of sales reps chasing spreadsheets, AI agents keep pipelines moving and up to date around the clock.
AI agents in operations and internal processes
Behind the scenes, many companies use AI agents to automate internal workflows such as:
- Invoice processing and reconciliation
- Employee onboarding tasks
- IT ticket triage
- Data cleanup and validation
These tasks often involve multiple systems and frequent exceptions, making them perfect candidates for agentic AI workflows.
Why these examples matter
What makes these AI agent examples powerful isn’t just speed. Agents don’t get tired, don’t forget steps, and don’t mind repetitive work. They simply execute toward their goal, again and again.
This is why many organizations now see AI automation tools not as productivity boosters, but as foundational infrastructure for modern operations.
Best AI agents and platforms available today
As interest in autonomous AI agents grows, a new ecosystem of platforms and tools has emerged. Some are designed for developers, others for non-technical teams, but all aim to reduce manual work through intelligent automation.
Rather than listing every tool on the market, it’s more useful to understand the main categories and what makes an AI agent platform “good.”
Developer-focused AI agent frameworks
These tools are designed for teams that want full control over how their agents behave. They’re often flexible, powerful, and a little technical.
Common features include:
- Custom goal definition and planning logic
- Tool and API integration
- Memory and context management
- Multi-agent coordination
These platforms are ideal if you want to build your own AI agent tailored to a specific workflow or product. They require setup, but the payoff is deep customization and scalability.
No-code and low-code AI automation tools
For businesses that want results quickly, no-code platforms make AI workflow automation accessible without heavy engineering work.
They typically offer:
- Visual workflow builders
- Prebuilt agent templates
- Easy integrations with popular tools
- Simple monitoring and controls
These AI automation tools are popular with startups and small teams looking to automate operations without hiring large development teams.
Enterprise AI agent platforms
Large organizations often need AI agents that can handle security, compliance, and scale. Enterprise platforms focus on:
- Role-based access and permissions
- Audit logs and monitoring
- Integration with legacy systems
- High reliability and uptime
For enterprises, AI agents for business are less about experimentation and more about replacing critical workflows safely.
What makes an AI agent “the best”
There’s no single answer to which platform is the best AI agent solution. It depends on your needs. However, strong platforms usually share a few traits:
- Clear goal-based design
- Reliable tool integration
- Transparency into agent decisions
- Human override and control options
The best AI agents feel predictable even when they’re autonomous. You know what they’re doing, why they’re doing it, and how to step in if needed.
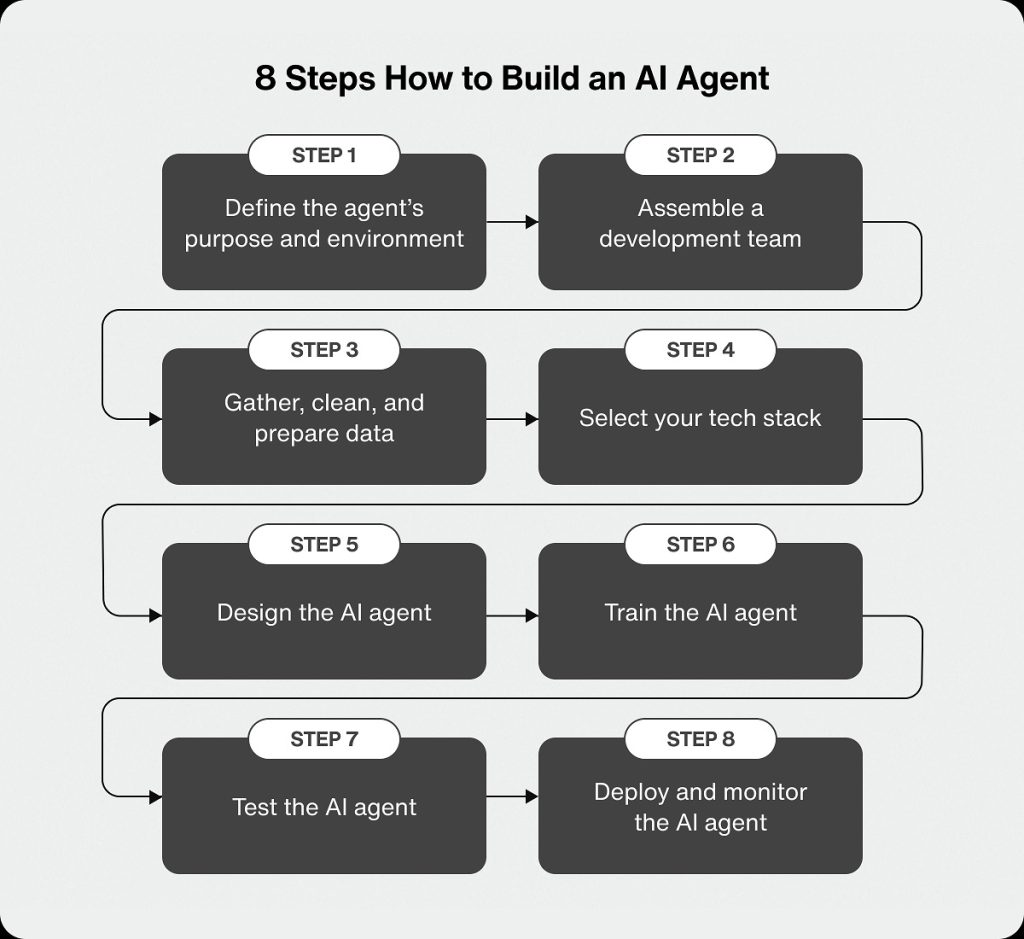
How to build your own AI agent
Building an AI agent might sound like something reserved for advanced developers or AI researchers. In reality, the barrier to entry has dropped significantly. Today, both technical and non-technical users can build agents that automate real work.
The key is understanding what level of complexity you actually need.
Step 1: Define a clear objective
Every successful agent starts with a well-defined goal. Vague objectives lead to unpredictable behavior, while clear goals produce reliable outcomes.
Good examples include:
- Monitor incoming leads and schedule follow-ups
- Keep project documentation up to date
- Generate weekly performance summaries
This step is crucial when learning how to build your own AI agent because the agent’s decisions will always trace back to this objective.
Step 2: Choose the right tools and data sources
AI agents become useful when they can interact with other systems. This might include:
- Email and messaging platforms
- CRMs and project management tools
- Databases and spreadsheets
- Internal knowledge bases
Modern AI automation tools make it easy to connect these services without writing large amounts of code.
Step 3: Set boundaries and rules
Autonomy doesn’t mean chaos. You need to define limits for what your agent can and cannot do. This includes:
- Which tools it can access
- When it should ask for human approval
- How it handles errors or uncertainty
Clear boundaries ensure your autonomous AI agents behave safely and predictably.
Step 4: Start simple, then expand
One of the biggest mistakes people make is trying to automate everything at once. Start with a small workflow, test it, and then expand.
For example, begin by having an agent draft responses rather than send them automatically. As confidence grows, you can increase autonomy.
Step 5: Monitor and refine
Even the best agents need oversight. Track performance, review decisions, and adjust goals or tools as needed. Over time, your agent becomes more aligned with how your business actually operates.
This gradual approach is why more teams are adopting agentic AI workflows without completely overhauling their systems overnight.
The future of AI agents and autonomous workflows
The rise of AI agents isn’t just a short-term productivity trend. It signals a deeper shift in how work gets done. Instead of humans managing tools, tools are increasingly starting to manage work on behalf of humans.
This transition is already underway, and its impact will only accelerate.
From task automation to outcome ownership
Early automation focused on tasks. Click this, move that, send this message. The future of AI agents is about outcomes. Businesses won’t automate individual steps anymore. They’ll delegate entire objectives.
For example, instead of automating invoice creation, a company may assign an agent the goal of “keeping billing accurate and up to date.” The agent decides how to achieve that outcome and adapts as conditions change.
This outcome-driven approach closely mirrors the next generation of personal AI assistants, where systems move beyond responding to commands and begin managing work proactively on behalf of users. It’s also why AI agents explained today will likely look basic compared to what’s coming in just a few years.
AI agents as digital coworkers
As agents become more reliable, they’ll start to resemble team members rather than tools. They’ll:
- Manage recurring responsibilities
- Coordinate with other agents
- Adapt to changing priorities
- Work continuously without burnout
For many organizations, this will feel like adding headcount without increasing payroll. That’s a major reason interest in AI agents for business is growing so quickly.
Impact on jobs and human roles
AI agents won’t eliminate work, but they will change it. Repetitive and administrative tasks will increasingly be handled by machines, while humans focus on:
- Strategy and decision-making
- Creative problem-solving
- Relationship management
- Oversight and governance
In other words, humans move up the value chain while agents handle the grind.
Regulation, trust, and control
With greater autonomy comes greater responsibility. The future will also bring:
- Stronger governance frameworks
- Clear audit trails for agent decisions
- Human-in-the-loop controls
- Ethical and compliance standards
The most successful companies will be those that balance autonomy with transparency and trust.
Conclusion: why AI agents are becoming unavoidable
AI agents are no longer experimental side projects or futuristic ideas. They’re practical, accessible, and already changing how work gets done. By moving from rigid rules to goal-driven systems, autonomous AI agents are replacing manual workflows that once required constant human oversight.
What makes this shift so powerful is not just efficiency, but flexibility. AI agents can adapt, learn, and operate across tools and platforms, making them far more capable than traditional automation or chatbots. For businesses, this means fewer bottlenecks, faster execution, and teams that can focus on higher-impact work.
As AI workflow automation continues to mature, the question won’t be whether to use AI agents, but how strategically they’re deployed. Those who start early, experiment responsibly, and build trust in agentic AI workflows will be best positioned for the future.
FAQs about AI agents
What are AI agents in simple terms?
AI agents are software systems that can observe information, make decisions, and take actions on their own to achieve a goal. Unlike basic automation, they don’t just follow fixed rules.
How are AI agents different from chatbots?
Chatbots respond to prompts and conversations. AI agents work toward objectives, plan multiple steps, and can act without being asked each time. That’s the key difference in AI agents vs chatbots.
Can small businesses use AI agents?
Yes. Many modern AI automation tools are designed for small teams and non-technical users. No-code platforms make it possible to deploy AI agents without heavy development work.
Are AI agents safe to use in business workflows?
When designed properly with boundaries, monitoring, and human oversight, AI agents can be very safe. Most businesses start with limited autonomy and expand as trust grows.
Will AI agents replace human jobs?
AI agents are more likely to replace repetitive tasks rather than entire roles. Humans remain essential for strategy, creativity, and oversight, while agents handle execution-heavy work.